







Evaluate ∫∫S1+x2+y2−−−−−−−−−√dS where S is the helicoid: r(u,v)=ucos(v)i+usin(v)j+vk, with 0≤u≤5,0≤v≤1π
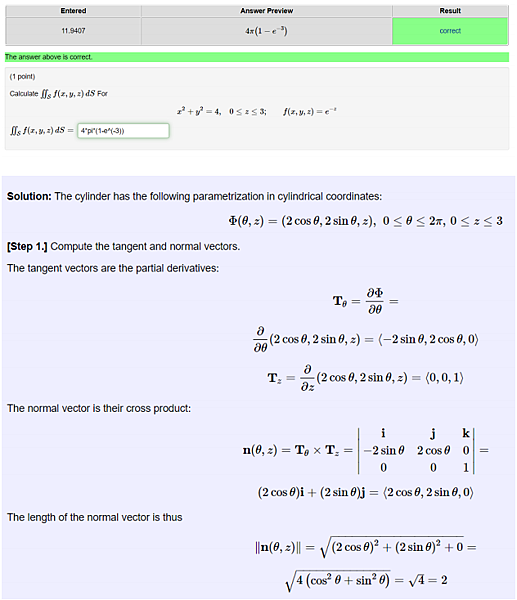
Calculate ∬Sf(x,y,z)dS For
∬Sf(x,y,z)dS=
Evaluate the integral with respect to surface area ∫∫T18xdA, where T is the part of the plane x+y+4z=6 in the first octant.
Evaluate the surface integral ∫SF⋅ dS where F=⟨3x,−4z,4y⟩ and S is the part of the sphere x2+y2+z2=4 in the first octant, with orientation toward the origin.
Evaluate the surface integral ∫SF⋅ dS where F=xyi+5x2j+yzk and S is the surface z=xey, 0≤x≤1,0≤y≤1, with upwards orientation.
Suppose F is a radial force field, S1 is a sphere of radius 2 centered at the origin, and the flux integral ∫∫S1F⋅dS=4.
Let S2 be a sphere of radius 6 centered at the origin, and consider the flux integral ∫∫S2F⋅dS.
Determine whether the flux of the vector field F⃗ (x,y,z)=zi⃗ through each surface is positive, negative, or zero. In each case, the orientation of the surface is indicated by the gray normal vector.





 留言列表
留言列表


