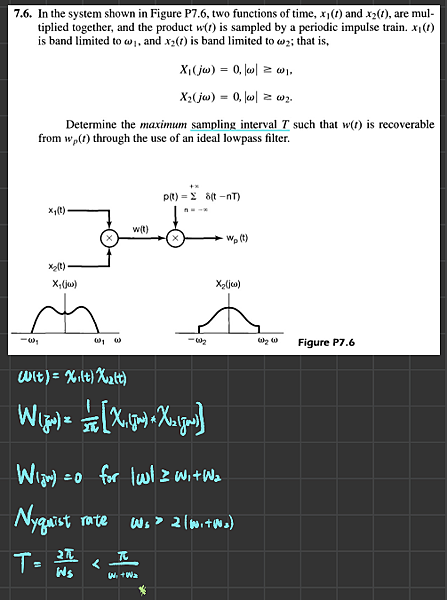


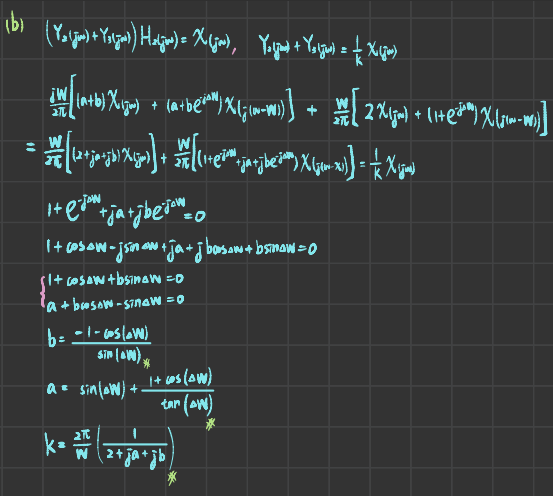

In the system shown in Figure P7.6, two functions of time, x_1(t) and x_2(t), are multiplied together and the product w(t) is sampled by a periodic impulse train. x_1(t) is band limited to omega_1, and x_2(t) is band limited to omega_2, that is, X_1(j omega) = 0, |omega| greaterthanorequalto omega_1, X_2(j omega) = 0, |omega| greaterthanorequal omega_2. Determine the maximum sampling interval T such that w(t) is recoverable from w_p(t) through the use of an ideal lowpass filter.
Shown in Figure P7.23 is a system in which the sampling signal is an impulse train with alternating sign. The Fourier transform of the input signal is as indicated in the figure. a) For< Tr/2m), sketch the Fourier transform of xp(t) and y(t). b For <Tr/(2M,determine a system that will recover xtfrom xpt. c For < T/2M),determine a system that will recover x(tfrom y(t. d) What is the maximum value of in relation to M for which x(t can be recov ered from either xp(t) or y(t)? p(t) xp(t) x(t) H(jw) y(t p(t) X(jw) UM H(jw) -3TT =T 3TT Figure P7.23
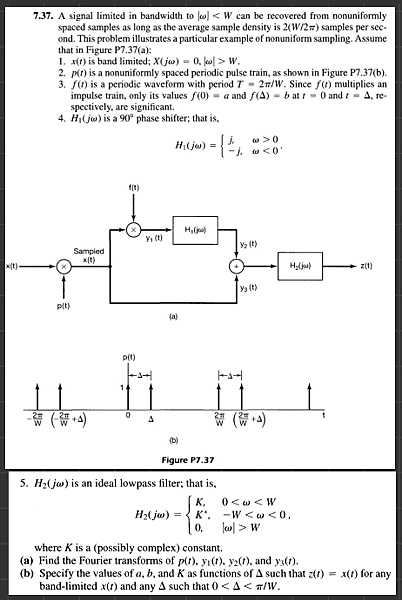
A signal limited in bandwidth to |omega| < W can be recovered from non-uniformly spaced samples as long as the average sample density is 2(W/2 pi) samples per second. Refer to the following figures and suppose x(t) is band-limited, i.e., X(j omega)) = 0 for |omega| > W; p(t) is the sampling impulse train; f(t) is a periodic waveform with period T = 2 pi/W. Since f(t) multiplies an impulse train, only its value f(0) = a and f(delta) = b are significant Hi(jo)) is a 90 degree phase shifter. Its frequency response is: H_1(j omega) = j for omega > 0 and H_1 (j omega) = - j for omega < 0 H_2(j omeag) is an ideal low pass filter. Its frequency response is: H_2(j omeag)) = K for 0 < omega < W; H_2(j omega) = K* for -W < omega < 0; and H_2(j omega) = 0 for |Omega| > W where K is a (possibly complex) constant Find the Fourier Transform of p(t), y_1(t), y_2(t), and y_3(t). You can specify the Fourier Transform of y_1(t), y_2(t), and y_3(t) over the range 0 < omega < W. Specify the values of a, b, and K as functions of A such that z(t) = x(t) for any band-limited x(t) and any A such that 0 < Delta < pi/W.
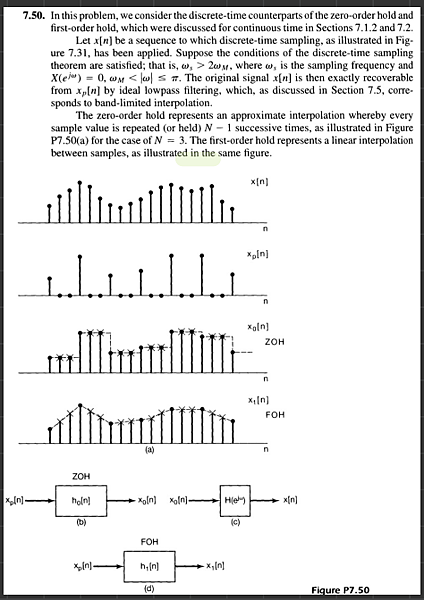
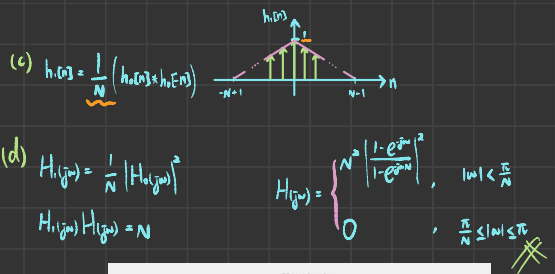
In this problem, we consider the discrete-time counterparts of the zero-order hold and first-order hold, which were discussed for continuous time in Sections 7 .1.2 and 7 .2. Let x[n] be a sequence to which discrete-time sampling, as illustrated in Figure 7.31, has been applied. Suppose the conditions of the discrete-time sampling theorem are satisfied; that is, ωs > 2ωM, where ωs is the sampling frequency and
X(ejω) = 0, ωM ≤ π. The original signal x[n] is then exactly recoverable from Xp[n] by ideal low pass filtering, which, as discussed in Section 7.5, corresponds to band-limited interpolation.
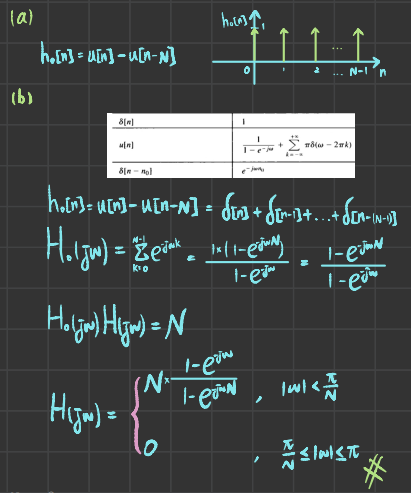
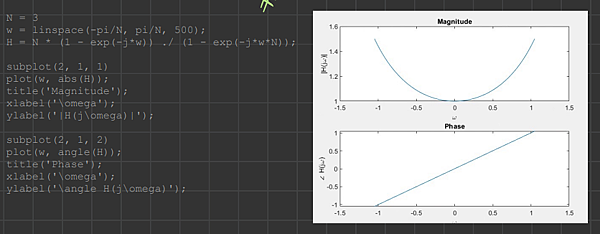
The zero-order hold represents an approximate interpolation whereby every sample value is repeated (or held) N - 1 successive times, as illustrated in Figure P7.50(a) for the case of N = 3. The first-order hold represents a linear interpolation between samples, as illustrated in the same figure.





 留言列表
留言列表


